Imagine being able to upload a screenshot of a business chart and have an AI system automatically analyze the data, extract key metrics, update your database, and generate an executive summary—all without writing a single line of code. This is the revolutionary capability that Zhipu AI’s GLM-4.6V brings to the table. Released in late September 2025, GLM-4.6V represents a quantum leap in multimodal AI technology by introducing native multimodal function calling directly from visual inputs.
As of November 2025, GLM-4.6V stands as one of the most advanced vision-language models available, featuring a 128K context window and native multimodal tool calling capabilities that enable it to autonomously orchestrate complex workflows. This guide will walk you through exactly how to leverage this groundbreaking technology to automate visual data processing tasks in your own projects.
Understanding GLM-4.6V’s multimodal function calling
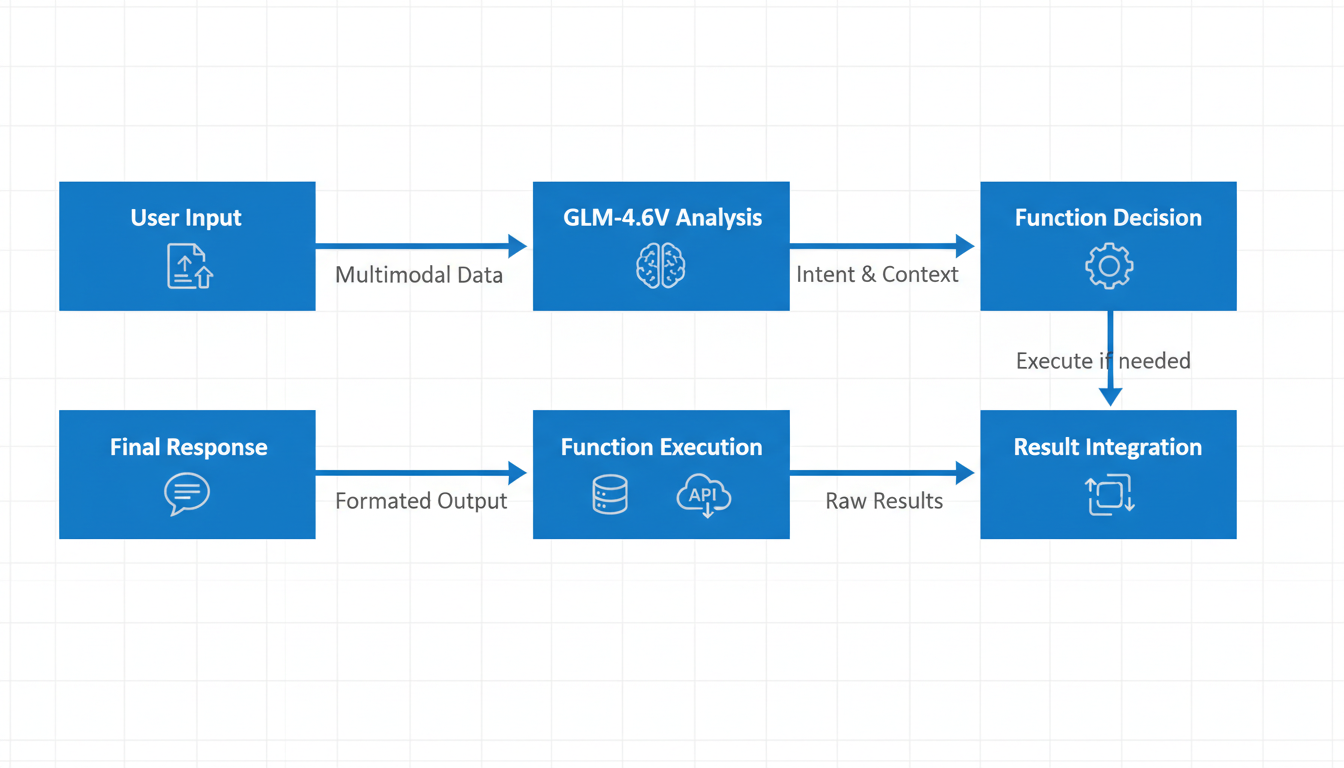
GLM-4.6V’s multimodal function calling differs fundamentally from traditional AI models. While most AI systems require explicit text-based instructions for function calls, GLM-4.6V can analyze images, screenshots, and document pages directly and autonomously decide which functions or APIs to invoke. According to Zhipu AI’s official documentation, this capability represents “native multimodal tool use” where the model can “pass images directly as input and trigger function calls based on visual analysis.”
The model achieves this through several key architectural innovations:
- Visual understanding integration: GLM-4.6V processes visual content through its vision encoder and integrates this understanding directly into its reasoning process
- Autonomous decision-making: The model can analyze visual inputs and determine which external tools or APIs would be most appropriate
- Structured output generation: GLM-4.6V outputs JSON-formatted function calls with precise parameters based on visual analysis
- Chain-of-thought reasoning: The model plans multi-step workflows involving both visual analysis and subsequent function execution
Setting up your development environment
Before diving into practical examples, you’ll need to set up your development environment with the necessary tools and API access.
Prerequisites and API access
To get started with GLM-4.6V multimodal function calling, you’ll need:
- A Zhipu AI API key (available through the Zhipu AI platform)
- Python 3.8+ installed on your system
- The Zhipu AI Python SDK
- Basic familiarity with Python programming
Install the Zhipu AI SDK using pip:
pip install zai-sdkVerify your installation:
import zai
print(zai.__version__)Basic API configuration
Configure your API client with the following basic setup:
from zai import ZaiClient
# Initialize client with your API key
client = ZaiClient(api_key='your_api_key_here')
# Verify connection
try:
response = client.models.list()
print("API connection successful")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Connection error: {e}")Practical implementation: Step-by-step tutorial
Let’s walk through three practical examples that demonstrate GLM-4.6V’s multimodal function calling capabilities.
Example 1: Automated chart analysis and data extraction
This example shows how GLM-4.6V can analyze a business chart image and automatically extract key metrics.
import base64
import json
from zai import ZaiClient
def encode_image_to_base64(image_path):
"""Convert image to base64 for API transmission"""
with open(image_path, "rb") as image_file:
return base64.b64encode(image_file.read()).decode('utf-8')
def update_database(metric_name, value, timestamp):
"""Simulate database update function"""
# Replace with actual database operations
print(f"Updating database: {metric_name} = {value} at {timestamp}")
return {"success": True, "metric": metric_name, "value": value}
# Define function tools for chart analysis
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "extract_chart_data",
"description": "Extract numerical values and trends from charts",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"chart_type": {"type": "string"},
"data_points": {"type": "array"},
"trend_analysis": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["chart_type", "data_points"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "update_database",
"description": "Update database with extracted metrics",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"metric_name": {"type": "string"},
"value": {"type": "number"},
"timestamp": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["metric_name", "value"]
}
}
}
]
# Analyze chart image
client = ZaiClient(api_key='your_api_key')
image_base64 = encode_image_to_base64("business_chart.png")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-4.6v",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Analyze this business chart and extract key performance metrics"},
{"type": "image_url", "image_url": {"url": f"data:image/jpeg;base64,{image_base64}"}}
]
}
],
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)Example 2: Inventory management via product images
GLM-4.6V can analyze product images and automatically update inventory systems.
def identify_product(image_analysis):
"""Identify product from visual analysis"""
# This would integrate with your product database
product_info = {
"name": "Smartphone X1",
"category": "Electronics",
"sku": "SPX1-2025",
"stock_level": 150
}
return product_info
def update_inventory(sku, quantity_change, operation_type):
"""Update inventory levels"""
print(f"Updating inventory: {sku} by {quantity_change} ({operation_type})")
return {"success": True, "sku": sku, "new_stock": 150 + quantity_change}
# Product identification tools
inventory_tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "identify_product",
"description": "Identify product from image and return SKU information",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"product_name": {"type": "string"},
"category": {"type": "string"},
"sku": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["product_name", "sku"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "update_inventory",
"description": "Update inventory system with new stock information",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"sku": {"type": "string"},
"quantity_change": {"type": "integer"},
"operation_type": {"type": "string", "enum": ["restock", "sale", "adjustment"]}
},
"required": ["sku", "quantity_change"]
}
}
}
]
# Process product image
product_image_base64 = encode_image_to_base64("product_photo.jpg")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-4.6v",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Identify this product and update inventory with +50 units"},
{"type": "image_url", "image_url": {"url": f"data:image/jpeg;base64,{product_image_base64}"}}
]
}
],
tools=inventory_tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)Example 3: Document processing and data entry automation
GLM-4.6V excels at processing document images and automating data entry workflows.
def extract_document_fields(document_analysis):
"""Extract structured data from documents"""
extracted_data = {
"invoice_number": "INV-2025-001",
"total_amount": 1250.50,
"vendor_name": "Tech Supplies Inc.",
"date": "2025-11-15"
}
return extracted_data
def create_accounting_entry(transaction_data):
"""Create accounting entry from extracted data"""
print(f"Creating accounting entry: {transaction_data}")
return {"success": True, "entry_id": "ACC-2025-001"}
# Document processing tools
document_tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "extract_document_fields",
"description": "Extract key fields from documents and invoices",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"document_type": {"type": "string"},
"extracted_fields": {"type": "object"}
},
"required": ["document_type", "extracted_fields"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "create_accounting_entry",
"description": "Create accounting system entry from extracted data",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"transaction_data": {"type": "object"}
},
"required": ["transaction_data"]
}
}
}
]
# Process document image
document_image_base64 = encode_image_to_base64("invoice_document.jpg")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-4.6v",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Extract invoice data and create accounting entry"},
{"type": "image_url", "image_url": {"url": f"data:image/jpeg;base64,{document_image_base64}"}}
]
}
],
tools=document_tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)Advanced techniques and best practices
To maximize the effectiveness of GLM-4.6V’s multimodal function calling, consider these advanced techniques.
Error handling and reliability
Implement robust error handling to ensure your automated workflows remain reliable:
def handle_function_call(response):
"""Robust function call handling with error management"""
try:
message = response.choices[0].message
messages = [message.model_dump()]
if message.tool_calls:
for tool_call in message.tool_calls:
try:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# Execute appropriate function
if function_name == "extract_chart_data":
result = extract_chart_data(arguments)
elif function_name == "update_database":
result = update_database(**arguments)
else:
result = {"error": f"Unknown function: {function_name}"}
# Add function result to conversation
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"content": json.dumps(result, ensure_ascii=False),
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id
})
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"content": json.dumps({"error": f"Invalid JSON: {str(e)}"}),
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id
})
except Exception as e:
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"content": json.dumps({"error": f"Function execution failed: {str(e)}"}),
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id
})
# Get final response with function results
final_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="glm-4.6v",
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)
return final_response.choices[0].message.content
else:
return message.content
except Exception as e:
return f"Error processing response: {str(e)}"Optimizing function definitions
Well-defined function specifications significantly improve GLM-4.6V’s performance:
# Optimal function definition example
optimal_tool = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "analyze_financial_chart",
"description": "Extract financial metrics from charts including revenue, growth rates, and key performance indicators",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"chart_type": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["bar", "line", "pie", "scatter"],
"description": "Type of chart being analyzed"
},
"time_period": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Time period covered by the chart data"
},
"key_metrics": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"metric_name": {"type": "string"},
"value": {"type": "number"},
"unit": {"type": "string"}
}
},
"description": "Extracted key performance metrics"
},
"trend_analysis": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["increasing", "decreasing", "stable", "volatile"],
"description": "Overall trend identified in the data"
}
},
"required": ["chart_type", "key_metrics", "trend_analysis"]
}
}
}Performance optimization
Consider these performance optimization strategies:
- Image preprocessing: Resize large images to reduce API payload size
- Batch processing: Process multiple images in single requests when possible
- Caching: Cache frequently analyzed images to reduce API calls
- Progressive loading: Use lower-resolution images for initial analysis
Real-world applications and use cases
GLM-4.6V’s multimodal function calling opens up numerous practical applications across industries.
Business intelligence automation
Automate the extraction of insights from business dashboards and reports. GLM-4.6V can analyze screenshots of analytics platforms and automatically update databases or generate reports.
E-commerce inventory management
Process product images to automatically update inventory systems, identify stock levels, and manage product catalogs without manual data entry.
Document processing workflows
Automate data extraction from invoices, receipts, forms, and other documents, reducing manual processing time and improving accuracy.
Quality control systems
Implement automated visual inspection systems that can analyze product images and trigger appropriate actions based on quality assessments.
Limitations and considerations
While powerful, GLM-4.6V’s multimodal function calling has some limitations to consider:
- API costs: High-volume image processing can become expensive
- Processing time: Complex visual analysis may take several seconds
- Accuracy limitations: Visual understanding may not be perfect for highly complex images
- Security considerations: Ensure sensitive images are handled appropriately
- Rate limits: Be aware of API rate limits for production applications
Future developments and trends
As of November 2025, multimodal function calling is still an emerging technology. We can expect several developments in the near future:
- Improved visual understanding: Enhanced accuracy for complex visual analysis
- Real-time processing: Faster analysis for time-sensitive applications
- Multi-modal chains: Integration with other AI capabilities like speech recognition
- Enterprise integrations: Deeper connections with business systems and workflows
Conclusion
GLM-4.6V’s multimodal function calling represents a significant advancement in AI capabilities, enabling automated visual data processing that was previously impossible or required extensive manual intervention. By following the techniques outlined in this guide, you can implement sophisticated automation workflows that leverage visual understanding to drive real business value.
The key takeaways for successful implementation include:
- Start with well-defined function specifications to guide the model’s decision-making
- Implement robust error handling to ensure reliability in production environments
- Optimize image processing to balance accuracy with performance and cost
- Focus on high-value use cases where visual automation provides significant efficiency gains
- Stay updated with Zhipu AI’s latest developments as the technology continues to evolve
As multimodal AI continues to advance, the ability to automate complex visual tasks will become increasingly accessible. GLM-4.6V provides a powerful foundation for building these next-generation automation systems today.