As of November 2025, every product manager is expected to “speak AI.” But there’s a gap: you’re told to build AI intuition, yet most RAG chatbot tutorials assume you can code. The good news is that modern no-code tools now let you prototype a serious RAG chatbot without writing a line of Python. That’s exactly what this guide covers: how RAG works in plain language, how to pick the right no-code stack, and a step-by-step walkthrough to ship a portfolio-ready RAG chatbot. By the end, you’ll not only have a working demo, but also the mental models to lead your next AI-driven project with confidence.
What RAG is (and why product managers should care)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) combines two things:
- A large language model (LLM) like OpenAI GPT-4.1 (released April 14, 2025) or Anthropic Claude Sonnet 4.x for natural language understanding and response.
- A retrieval layer (usually a vector database like Pinecone, whose latest stable API version is 2025-10 as of November 19, 2025) that searches your documents and feeds the most relevant snippets into the LLM at query time.
Instead of the model “guessing” from its training data, RAG makes it quote from your actual knowledge base: PDFs, help center articles, product specs, or company policies.
- For product managers, RAG is the backbone of practical AI features: knowledge assistants, support bots, sales enablement tools, and internal copilots.
- Prototyping a RAG chatbot with no-code is one of the fastest ways to build AI product intuition: you’ll touch data ingestion, retrieval quality, evaluation, and UX tradeoffs.
The no-code RAG stack for product managers (2025)
There are many AI builders in 2025, but most PMs don’t need a huge platform just to ship a portfolio demo. You want:
- No-code / low-code canvas to orchestrate the flow visually.
- Hosted LLMs (you just paste an API key).
- Built-in or easy vector DB so you don’t manage infra.
- Simple web embed so you can share your chatbot.
Two leading visual builders for agentic and RAG apps as of late 2025 are:
- Langflow 1.6+ (released October 2, 2025): open-source, Python-based, with a visual flow editor, strong RAG components, and advanced document parsing via Docling. Excellent for structured RAG experimentation.
- Flowise 3.0.11 (latest GitHub release in 2025): open-source, visual “nodes and edges” builder with built-in support for OpenAI GPT-4.1, Claude 4 models, vector stores, and OpenAI-compatible APIs.
For a PM with no coding background, you can use either. This guide will assume you use Langflow (for its RAG-focused templates and clear documentation), but the product thinking applies equally if you pick Flowise or a commercial no-code chatbot builder that supports RAG.
| Component | Recommended option (as of Nov 2025) | Why it’s PM-friendly |
|---|---|---|
| No-code RAG builder | Langflow 1.6+ | Visual editor, RAG templates, advanced file parsing, OpenAI-compatible API for easy embedding |
| LLM | OpenAI GPT-4.1 or GPT-4.1 mini | Strong reasoning and coding, widely documented; mini is cheaper for prototypes |
| Vector database | Pinecone Assistant / serverless index | Fully managed, strong docs and tooling, optimized for RAG workloads in 2025 |
| Front-end chat UI | Langflow Playground embed or lightweight web page | Allows you to share a live demo without engineering support |
You don’t need to master all of these deeply to build a great portfolio RAG chatbot. You do need to understand what each one does and how they fit together.
Architecture: how a no-code RAG chatbot works end-to-end
Before touching any tools, internalize this flow. It’s the mental model you’ll reuse in every AI project.
- User asks a question in your chat UI.
- Orchestrator (Langflow) receives the query and triggers a RAG flow.
- Embedding & retrieval: The query is converted to an embedding and used to search a vector database (e.g., Pinecone) that stores your document chunks.
- Reranking / filtering: Optionally, you refine which chunks are most relevant.
- Prompt construction: The orchestrator builds a structured prompt for the LLM, inserting the retrieved context snippets plus instructions.
- LLM response: GPT-4.1 (or another model) generates an answer, citing sources if configured.
- Response returned to UI: The orchestrator streams or returns the answer to your chat interface.
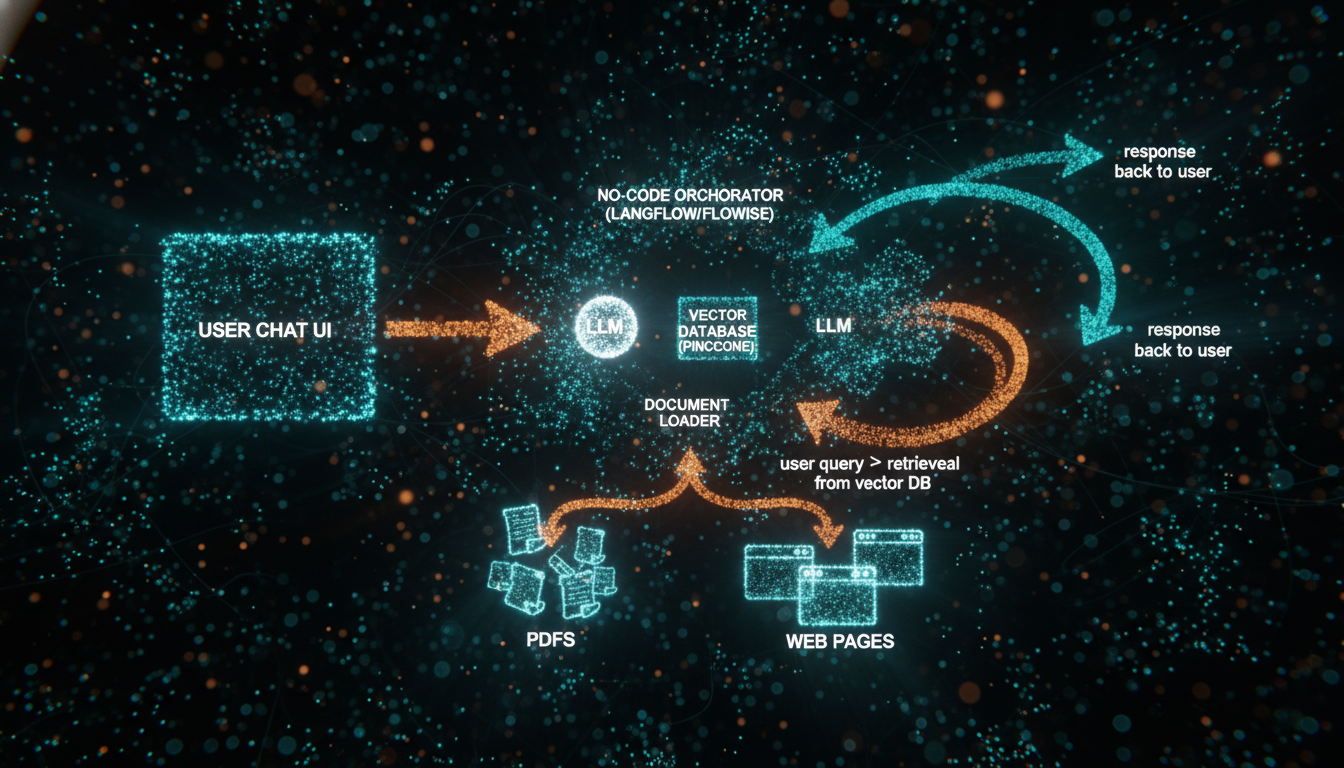
From a PM perspective, each arrow in this diagram maps to a product decision: where you allow user uploads, how often you refresh data, how you handle low-confidence answers, and how you log interactions for improvement.
Step-by-step: building your first RAG chatbot with Langflow (no code)
This walkthrough assumes you’re building a portfolio-ready chatbot that answers questions about a product or company knowledge base. You’ll focus on shipping something real, not a toy demo.
Step 1: Clarify your use case and success criteria
Before tools, decide what “good” looks like. A tight use case will impress more than a vague “ask me anything” bot.
- Scope: e.g., “Answer questions about our B2B SaaS pricing, SLAs, and core features.”
- Audience: PM interviewers, internal sales team, or customers?
- Success criteria (simple, measurable):
- At least 80% of common FAQs answered correctly.
- Responses always show which document they came from.
- The bot never fabricates pricing or legal terms; it says “I’m not sure” instead.
“Defining a narrow, verifiable scope is the single highest-leverage decision you can make as a PM building a RAG chatbot.”
AI product intuition principle
Step 2: Collect and clean your source documents
RAG quality is mostly a data problem, not a model problem. Curate a small but clean corpus:
- Product one-pagers and pitch decks (PDF, PPTX).
- Pricing and packaging sheets.
- FAQ docs, onboarding guides, support articles.
- SLAs, terms summaries (avoid full legalese if possible).
- Normalize formats: Convert to PDF or markdown where possible.
- Remove noise: Delete pages with only marketing fluff, stock images, or outdated references.
- Version control: Mark each document with a clear version/date so your bot can communicate recency.
Langflow 1.6 includes advanced parsing via Docling, allowing robust extraction from messy PDFs and images directly in the File component. As a PM, this means you can comfortably ingest “real” assets instead of hand-crafted samples.
Step 3: Set up Langflow and connect an LLM
- Install or access Langflow
- Download Langflow 1.6 desktop app from the official site, or run the hosted/desktop version if available.
- Generate an LLM API key
- Create an OpenAI account and get an API key that supports GPT-4.1 or GPT-4.1 mini (model family introduced April 14, 2025).
- Configure Langflow to use your LLM
- In Langflow’s settings, add the OpenAI API key and select GPT-4.1 (or mini) in the language model component when you build the flow.
Concept to internalize: you’re not “installing a model”; you’re renting one via an API. Your orchestration (Langflow) controls what the model sees and how it behaves.
Step 4: Build the RAG pipeline visually
Now you’ll create the actual RAG flow in Langflow’s visual editor.
- Create a new flow
- Choose a blank project or, if available, start from a “RAG chatbot” template to accelerate setup.
- Add a File or Data Loader component
- Upload your curated PDFs and docs.
- Enable the Advanced Parser setting (Docling) for messy PDFs to produce clean text or markdown.
- Chunk and embed documents
- Configure a chunking strategy (e.g., 500–1000 characters with overlap) to balance granularity and coherence.
- Choose an embedding provider (OpenAI or another provider supported by Langflow) to convert text chunks to vectors.
- Connect to a vector store
- Either use Langflow’s built-in vector store, or connect to Pinecone (using its latest 2025-10 API) via the appropriate component.
- Decide on index parameters (dimension, metric) as guided by the embedding model defaults.
- Configure retrieval
- Add a retrieval node that queries the vector store using the user’s question.
- Set
top_k(how many chunks to retrieve) and filters if needed (e.g., only pricing docs).
- Design the prompt construction
- Use a prompt template that:
- Instructs the model to answer only from provided context.
- Includes space for context snippets.
- Requires the model to say “I don’t know” when context is insufficient.
- Use a prompt template that:
- Connect to the LLM node
- Wire the prompt template output into the GPT-4.1 (or chosen LLM) component.
- Expose a Chat UI
- Use Langflow’s Playground to test the flow as a chatbot.
- Later, publish the flow as an API endpoint or embedded widget.
# Example RAG prompt template (for GPT-4.1)
You are a helpful assistant that answers questions about <PRODUCT_NAME>.
Use ONLY the information in the <CONTEXT> section to answer.
If the answer is not in the context, say:
"I don't know based on the current documentation."
Always:
- Be concise (3–6 sentences).
- Quote the document title and section when possible.
<CONTEXT>
{{ context }}
</CONTEXT>
User question: {{ question }}Even without code, you’re designing the system’s behavior through configuration and prompts. This is core AI product work.
Step 5: Test, evaluate, and iterate like a PM
Once the flow runs, resist the urge to immediately polish the UI. Treat this like a mini product launch.
- Create a test set
- Write 20–30 representative user questions across topics: pricing, integrations, SLAs, edge cases.
- Run them through your chatbot
- Log the answer, whether it was correct, and whether sources were cited.
- Diagnose failure modes
- Hallucinations: tighten instructions, reduce creativity (temperature), demand citations.
- Missed answers despite docs present: adjust chunk size, increase
top_k, or improve embeddings/vector DB settings. - Overly long answers: add length constraints or bulleted response format.
- Iterate
- Update chunking, retrieval parameters, and prompts.
- Re-test the same question set to measure improvement.
Your goal isn’t perfection; it’s to demonstrate that you understand how to diagnose and shape RAG behavior: a key AI PM skill.
Step 6: Ship a shareable demo for your portfolio
To make this project interview-ready, wrap your RAG chatbot in a simple, polished experience.
- Publish the flow: Use Langflow’s API publishing or OpenAI-compatible responses API endpoint (
/api/v1/responsesin 1.6) to expose your chatbot as a simple HTTP endpoint. - Create a minimal web UI: If you’re non-technical, collaborate with a designer or use a lightweight website builder to embed a chat widget that talks to your Langflow endpoint.
- Write a product-style README: Include problem statement, target user, scope, architecture diagram, and key decisions (models used, vector DB choice, data sources).
- Capture screenshots or a short loom: Demo the RAG chatbot answering real questions, including failures and how you’d improve them.

Tool choices and tradeoffs: thinking like an AI PM
Even if you never touch code, you’ll be expected to make smart tradeoffs across tools. Use your prototype to practice articulating them.
- LLM choice
- GPT-4.1: better reasoning and tool use, higher cost; ideal for complex enterprise use cases.
- GPT-4.1 mini: cheaper, faster; good for FAQs and prototyping.
- Claude 4.x family (Opus, Sonnet, Haiku 4.5): strong coding & long-context; may be preferable where Anthropic is the company standard.
- Vector DB choice
- Langflow’s built-in store: easiest for demos, minimal setup.
- Pinecone: better path to production; in 2025 it adds features like dedicated read nodes, metadata schema management, and improved sparse/lexical search.
- No-code vs low-code
- Pure no-code (Langflow, Flowise canvas only) is fastest to learn, ideal for your first prototype.
- Low-code (small scripts, custom components) unlocks advanced logic but requires engineering support or upskilling.
In interviews, explain not just what you chose, but what you deliberately did not optimize yet (e.g., no multi-tenant security, manual evaluation rather than automated metrics).
From one-off chatbot to repeatable AI product intuition
Your first no-code RAG chatbot is more than a neat demo; it’s a sandbox for becoming an AI-first PM. As of late 2025, successful AI PMs consistently show they can:
- Translate ambiguous business needs (“We need smarter support”) into concrete AI workflows (RAG + guardrails + logging).
- Prototype quickly with tools like Langflow or Flowise to validate feasibility before involving engineering.
- Reason about data quality and retrieval performance, not just “pick the latest model.”
- Communicate architecture clearly to both executives and developers with diagrams and structured docs.
To deepen your AI product intuition after this project:
- Clone your RAG setup for a different domain (e.g., HR policy bot, sales playbook assistant) and compare behavior.
- Experiment with different models (GPT-4.1 vs Claude Sonnet 4.x) keeping the same data to isolate model differences.
- Add basic analytics: track queries where the model says “I don’t know,” and treat them as backlog items for documentation or data improvements.
If you can walk into your next interview and show: (1) a live RAG chatbot, (2) a clear explanation of the architecture, and (3) a thoughtful discussion of tradeoffs and failures, you’ll be far ahead of most candidates. No code required, but plenty of product judgment on display.




