As of November 2025, the most serious failures in enterprise generative AI rarely come from “bad models.” They come from weak or removable AI guardrails: missing content filters, jailbreak-prone prompts, unsafe tool access, and no monitoring. When developers or ops teams can simply switch off safety layers to “debug” or ship faster, you inherit an unbounded security, compliance, and reputational risk. This guide is an evergreen, technical walkthrough for developers and MLOps teams on how to implement robust AI guardrails for LLM deployments, using current tools like NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails 0.18.0 (released 2025), Meta’s Llama Guard 4 (released April 2025), Azure AI Content Safety (docs updated Nov 2025), and Google Vertex AI’s safety filters (updated Nov 2025). You’ll learn how to design, implement, and operate multilayer guardrails that keep LLMs secure and enterprise-ready without suffocating innovation.
Understand AI guardrails and the 2025 risk landscape
AI guardrails are technical and process controls that constrain what LLMs can see, do, and say. They sit around and above the model, not just inside it. The 2025 OWASP Top 10 for LLMs highlights why this matters: prompt injection (LLM01:2025) remains the top risk, followed by sensitive information disclosure, supply chain issues, data/model poisoning, improper output handling, excessive agency, system prompt leakage, vector store weaknesses, misinformation, and unbounded resource consumption. Guardrails must explicitly address these classes of risk.
In practice, effective AI guardrails span four dimensions:
- Content safety: prevent harmful, non-compliant, or policy-violating inputs and outputs.
- Capability safety: constrain which tools, data, and actions the model can trigger (agency control).
- Data protection: minimize and mask sensitive data, prevent leakage via responses or logs.
- Operational safety: rate limits, cost controls, monitoring, evaluation, and incident response.
Design a multilayer LLM security architecture
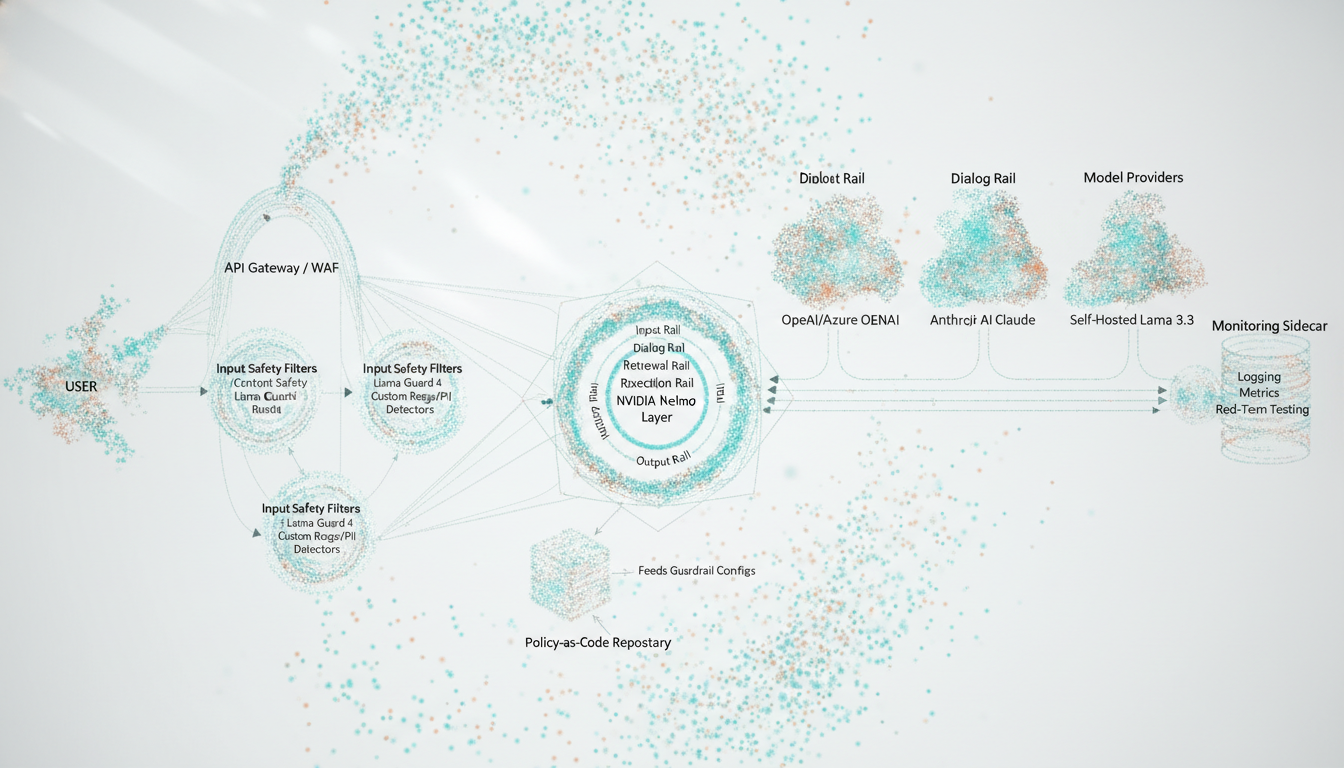
Before you write code, design the guardrail stack. A robust architecture typically has these layers:
- Perimeter & API protection: WAF, API gateway, authN/Z, basic input size & rate limits.
- Input content safety: classification and blocking of unsafe prompts (e.g., Azure AI Content Safety, Llama Guard 4, Vertex AI safety filters).
- Conversation & tool orchestration guardrails: frameworks like NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails 0.18.0 to control intent, topics, and tool use.
- Output content safety: post-generation filters to catch unsafe or hallucinated responses.
- Data & vector store protection: PII masking, tenant isolation, policy-aware RAG retrieval.
- Monitoring, evaluation & red-teaming: logs, metrics, safety scorecards, continuous tests.
Critically, guardrails must not be optional in production. They should be treated as security controls, enforced via infrastructure (e.g., only a guarded microservice can talk to the model endpoint) and policy-as-code (gated in CI/CD).
Choose your guardrail components (2025 ecosystem)
As of late 2025, several mature options exist:
| Guardrail layer | Representative tools (latest noted) | Key capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Programmable guardrails & orchestration | NeMo Guardrails 0.18.0 (beta) | Input / dialog / retrieval / execution / output rails; LangChain & LangGraph integration; content safety & jailbreak NIMs |
| Open-source safety classifiers | Llama Guard 4 (12B, Apr 2025), Prompt Guard 2, LlamaFirewall | Multimodal safety classification, prompt attack detection, orchestrated firewall for agents and tools |
| Cloud-native filters | Azure AI Content Safety (2024–2025 APIs), Vertex AI safety filters & jailbreak classifier (Gemini 2.5 Flash) | Text/image/multimodal moderation, prompt shields, groundedness, protected material, task adherence |
| Model providers’ built-ins | OpenAI / Azure OpenAI safety policies, Anthropic Constitutional Classifiers (2025), Llama Moderations API | Default usage policies, classifier-based refusal, model-aligned safety policies |
Your architecture should combine at least one programmable guardrails framework (e.g., NeMo Guardrails or LlamaFirewall) with at least one classifier (e.g., Llama Guard 4 or Azure Content Safety) and native cloud safety features where you run the models.
Implement content safety guardrails end-to-end
Content safety is the first guardrail most teams implement. The goal is to enforce consistent policies on both prompts and responses, using standardized taxonomies (MLCommons hazards, Azure harm categories, etc.) and to make those policies configurable per app or tenant.
Step 1: Define policy as code
Start with a written safety policy: what your LLM app must block, what it may allow, and what needs human review. Then encode this policy in machine-readable form so you can apply it consistently across tools.
- Use a category-based taxonomy, e.g. MLCommons hazards (S1–S14 in Llama Guard 4) or Azure’s harm categories (sexual, violence, hate, self-harm).
- Store thresholds and rules in a versioned config (YAML, JSON) and load them into your guardrails framework or microservices.
- Bind each category to actions: block, mask, rewrite, route to human, log-only.
# Example: safety-policy.yml (simplified)
harm_categories:
sexual_content:
sources: [azure_text, llama_guard4]
threshold: block_above=medium
action: block
violence:
sources: [azure_text]
threshold: block_above=high
action: block_or_rewrite
pii:
sources: [llama_guard4, regex_pii]
threshold: block_above=low
action: mask
elections:
sources: [llama_guard4]
threshold: block_any
action: escalate_to_humanStep 2: Wire in pre‑model input safety checks
Before a prompt reaches any LLM, pass it through a content safety service. For example, using Azure AI Content Safety’s AnalyzeText API (GA with latest docs updated Nov 2025):
import os
import requests
AZURE_ENDPOINT = os.environ["AZURE_CONTENT_SAFETY_ENDPOINT"]
AZURE_KEY = os.environ["AZURE_CONTENT_SAFETY_KEY"]
def analyze_text(prompt: str) -> dict:
url = f"{AZURE_ENDPOINT}/contentsafety/text:analyze?api-version=2024-09-01"
headers = {
"Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key": AZURE_KEY,
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
payload = {
"text": prompt,
"categories": ["Hate", "Violence", "Sexual", "SelfHarm"],
"outputType": "EightSeverityLevels"
}
resp = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers, timeout=3)
resp.raise_for_status()
return resp.json()
def enforce_input_policy(prompt: str) -> str | None:
result = analyze_text(prompt)
for cat in result["categoriesAnalysis"]:
severity = cat["severity"]
if cat["category"] == "Sexual" and severity >= 3: # example rule
return None # block
return promptIn GCP, configure Gemini / Vertex AI safety with per-category thresholds using HarmBlockThreshold and SafetySetting. For example, block low-and-above harassment while turning off sexual filtering for an internal red-team tool.
Step 3: Add Llama Guard 4 as a cross‑provider safety layer
Llama Guard 4 (12B, released April 29, 2025) is a multimodal safety classifier trained on the MLCommons hazards taxonomy. It can run on a single GPU or via the Llama Moderations API. To use it as a local guardrail for any model:
from transformers import AutoProcessor, Llama4ForConditionalGeneration
import torch
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-Guard-4-12B"
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
model = Llama4ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
model_id, device_map="cuda", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
)
def llama_guard_check(text: str) -> dict:
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": text}]}]
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages, tokenize=True, add_generation_prompt=True,
return_tensors="pt", return_dict=True
).to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=16, do_sample=False)
response = processor.batch_decode(
outputs[:, inputs["input_ids"].shape[-1]:],
skip_special_tokens=True
)[0].strip()
# Response format: "safe" or "unsafe\nS1,S2"
lines = response.splitlines()
verdict = lines[0]
categories = lines[1].split(",") if len(lines) > 1 else []
return {"verdict": verdict, "categories": categories}You can then enforce your YAML policy by mapping S1–S14 categories to your internal categories and deciding whether to block, mask, or log.
Step 4: Integrate NeMo Guardrails content safety flows
NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails 0.18.0 provides content-safety flows that call safety models (including NVIDIA’s own NemoGuard content safety NIMs). The official docs (release notes updated Nov 2025) show a working example where the main generation model is Llama 3.3 70B Instruct and the content safety model is Llama‑3.1‑Nemoguard‑8B.
# config/config.yml
models:
- type: main
engine: nvidia_ai_endpoints
model: meta/llama-3.3-70b-instruct
- type: content_safety
engine: nvidia_ai_endpoints
model: nvidia/llama-3.1-nemoguard-8b-content-safety
rails:
input:
flows:
- content safety check input $model=content_safety
output:
flows:
- content safety check output $model=content_safety
streaming:
enabled: true# app.py
from nemoguardrails import LLMRails, RailsConfig
config = RailsConfig.from_path("./config")
rails = LLMRails(config)
def generate_guarded(messages):
return rails.generate(messages=messages)This pattern externalizes safety into explicit flows (Colang definitions + prompts) that your security team can review and extend without changing app code.
Control tools, actions, and data access (“capability guardrails”)
Many of the most dangerous failures are not what the model says, but what it does: invoking tools, calling APIs, running code, or modifying records. OWASP’s 2025 category “Excessive Agency” covers exactly this. Your guardrails must wrap tool calling and RAG, not just text.
Step 5: Guard tool usage and agents
Use an orchestration layer (NeMo Guardrails, LlamaFirewall, or a custom policy engine) that sits between the LLM and tools:
- Define an allow-list of tools per agent and per tenant.
- Require explicit capability checks before tool execution (e.g., “is user authenticated?”, “is resource in allowed scope?”).
- Use policy-as-code (e.g., Open Policy Agent/Rego) to approve or deny tool invocations based on attributes.
- Log every tool call with input, output, and the decision that allowed it.
# Pseudocode: policy check before a tool call
def guarded_tool_call(user, tool_name, args):
decision = opa_client.evaluate(
policy="llm/tool_access.rego",
input={"user": user, "tool": tool_name, "args": args}
)
if not decision["allow"]:
raise PermissionError("Tool call blocked by policy")
return tools[tool_name](**args)NeMo Guardrails 0.17.0–0.18.0 added LangGraph and tool-calling support so you can intercept, store, and forward tool invocations inside multi-agent workflows, applying guardrails at graph boundaries.
Step 6: Secure RAG pipelines and vector stores
OWASP LLM08:2025 warns about vector and embedding weaknesses. RAG pipelines can leak data or be poisoned if you don’t guard them.
- Tenant isolation: separate indexes per tenant or include tenant IDs in filters; never cross-query by default.
- Document-level ACLs: filter retrievals by user/role before embedding or at query time.
- Content safety on retrieved chunks: use “retrieval rails” (NeMo) or classifiers to drop unsafe chunks before they hit the prompt.
- Embedding validation: sanitize and normalize text before embedding; watch for outlier embeddings or anomalous similarity spikes.
# Example NeMo retrieval rail (conceptual Colang)
define flow
user asks question
retrieve documents
filter documents with content_safety
bot answers using filtered documentsOperationalize guardrails in CI/CD and runtime
Guardrails only reduce risk if they’re enforced consistently in every environment and change is controlled. Treat them like security middleware, not like optional SDK flags.
Step 7: Make guardrails non‑removable in production
Key patterns:
- Network-level enforcement: Only a guarded service identity (e.g.,
llm-proxy) can call external LLM APIs. Apps talk to the proxy, not directly to OpenAI/Gemini/Claude. - Immutable configuration paths: Production guardrail configs come from a Git repository, pinned to a commit hash via CI/CD. No ad-hoc runtime overrides.
- Environment segregation: Allow loosening guardrails only in isolated sandboxes or red-team environments, with separate projects/keys.
- Policy gates: Break the build or block deployment if guardrail tests fail or policy coverage drops.
Step 8: Add observability and safety analytics
NeMo Guardrails 0.16.0+ provides OpenTelemetry-based tracing of guardrail decisions and events, including reasoning traces for advanced models. Azure Content Safety Studio and Vertex AI Studio offer dashboards for moderation traffic and categories.
- Instrument every guardrail decision with: model, category, verdict, action, latency, and correlation IDs.
- Emit metrics such as: block rates by category, false positive/negative estimates, prompt injection attempts per hour, tool-call denials, cost per request.
- Pipe logs to a SIEM; define alerts for unusual spikes (e.g., sudden surge in jailbreak attempts or new hazard categories triggered).
# Example: logging a safety decision (Python pseudocode)
logger.info(
"safety_decision",
extra={
"request_id": req_id,
"user_id": user_id,
"source": "llama_guard4",
"verdict": result["verdict"],
"categories": result["categories"],
"action": "blocked" if blocked else "allowed",
},
)Step 9: Continuous evaluation and red‑teaming
Static guardrail configs will drift out of effectiveness as attacks evolve. Build a repeatable evaluation loop:
- Assemble test suites: include OWASP-aligned cases (prompt injection, system prompt leakage, excessive agency, data exfiltration) plus your domain-specific misuse scenarios.
- Use vendor eval tooling: NeMo’s
nemoguardrails evaluate, Meta’s CyberSecEval 4 and prompt injection benchmarks, Azure’s groundedness and protected-material evaluators, Vertex AI’s evaluation SDK. - Automate regression tests: run them in CI whenever you change prompts, policies, or models.
- Track key safety KPIs: unsafe prompts blocked %, benign prompts incorrectly blocked %, jailbreak success rate, time-to-detect incidents.

Example: end‑to‑end guarded LLM proxy service
Putting it together, a common pattern is a “guarded proxy” microservice fronting all LLM providers:
- Receives a chat or completion request from internal apps.
- Runs input through: size/rate limits → Azure/Vertex filters → Llama Guard 4 → NeMo input rails.
- Calls the configured LLM (OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, or self-hosted Llama 3.3).
- Runs the response through NeMo output rails, Llama Guard 4, and possibly groundedness / fact-checking.
- Returns a safe, possibly rewritten response plus safety metadata.
# Simplified guarded proxy handler
def handle_chat(request):
user = authenticate(request)
messages = request.json["messages"]
# 1) Basic checks
enforce_rate_limit(user)
validate_schema(messages)
# 2) Input safety (Azure + Llama Guard 4)
user_text = messages[-1]["content"]
if not enforce_input_policy(user_text):
return error("Prompt violates safety policy")
lg_result = llama_guard_check(user_text)
if lg_result["verdict"] == "unsafe":
return error(f"Prompt unsafe: {lg_result['categories']}")
# 3) NeMo input/dialog rails
guarded_response = rails.generate(messages=messages)
# 4) Post-output safety
out_text = guarded_response["content"]
if not enforce_output_policy(out_text):
return error("Output blocked by safety policy")
lg_out = llama_guard_check(out_text)
if lg_out["verdict"] == "unsafe":
return error(f"Output unsafe: {lg_out['categories']}")
log_safety_decisions(...)
return {"role": "assistant", "content": out_text}This proxy can be deployed behind your API gateway and scaled horizontally. Because all safety logic is centralized, you avoid each product team reinventing (or accidentally disabling) guardrails.
Conclusion: make guardrails a first‑class part of LLM engineering
Robust AI guardrails are now a non‑negotiable requirement for enterprise LLM deployments. OWASP’s 2025 Top 10 makes it clear that threats like prompt injection, sensitive data leakage, excessive agency, and misinformation are systemic risks, not edge cases. The good news: with modern frameworks (NeMo Guardrails 0.18.0, Llama Guard 4, LlamaFirewall) and cloud-native content safety services (Azure AI Content Safety, Vertex AI safety filters, Anthropic constitutional classifiers), you can implement multilayer protections without crippling developer velocity.
To move forward:
- Codify your safety and compliance requirements into a category- and threshold-based policy.
- Deploy a guarded proxy or orchestration layer that all LLM traffic must pass through.
- Combine input and output content filters with strict tool/RAG controls and observability.
- Integrate safety evaluation and red-teaming into CI/CD so guardrails evolve with attacks.
Treat guardrails like you treat authentication, encryption, and network segmentation: mandatory, tested, and owned jointly by security and engineering. Done well, AI guardrails don’t stifle innovation; they create the confidence you need to scale LLMs across your organization.




